In this tutorial, you will learn about the do-while loop in the C++ programming language with the help of examples.
In C++, do-while Loops are used when you do not know how many times the loop will execute but you need it to execute for a minimum of once. It is a type of while loop but the statements are executed first and then the condition is tested. For and While are entry controlled loops but do-while is an exit controlled loop.
Syntax
The syntax for the do-while loop is as follows:
Initialization of the expression
do
{
// loop body which will be executed at least once.
update_expression;
}
while (test or condition expression);
On breaking down the different parts of a for loop we will get the following :
- Initialization Expression: This expression is used to initialize the do-while loop with an initial value by either declaring and initializing a variable there or only by initializing an existing variable at that point. It is declared outside the body of the loop. For example,
int i=6;orj=k// Provided bothjandkhave been declared andkhas been initialized.
- Update Expression: This expression will get executed before the statements in the do-while loop have been executed and before the loop condition is evaluated. It will execute as many times as the do-while loop statement will get executed and it can be mentioned anywhere in the do-while block. Eg.
i++; - Test or Exit Condition: This expression will keep on getting executed until the condition is false and then the program flow will move out of the do-while loop. If the condition is true, it will move into the block and execute the statements inside the do-while loop. Even if the condition is false from the beginning, the block will get executed at least once. Eg.
i<10;
Flowchart of Do While Loop in C++
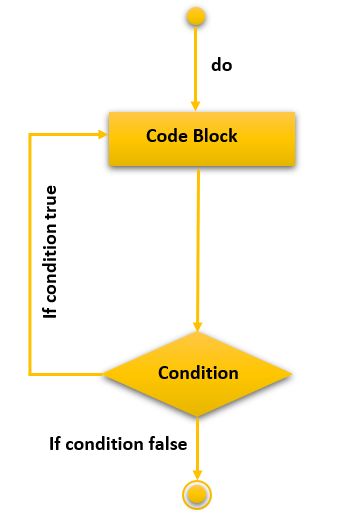
The Structure of Do-While Loop Execution
The “Do-While Loop” execution follows the following pattern of code execution which are as follows:
- Execution begins by initialization
- The loop block and the update statement are executed.
- After the update, the control moves to the condition statement in the next step
- The execution moves onto the condition of the do-while loop.
- If the condition is true, the flow moves onto the body.
- If the condition is false, the flow moves to the outside of the body of the loop.
- The above statements from steps 4 to 2 are repeated till the condition is false and it exits from the block.
Example
//A C++ program to show how a do-while loop works
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Initialization of the expression
int i = 2;
do {
// Loop body statement
cout << "Hello World\n";
// Update the expression
i++;
}while (i < 1); // Condition expression. There is a semi-colon after while.
return 0;
}
Output
Program Flow
- Program starts.
iis initialized to 2.- Execution enters the loop.
a) “Hello World” gets printed 1st time.
b) Updation is done. Nowi = 2. - Condition is checked. 2 < 2 yields false.
- The flow goes outside the loop.
Example: 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Initialization expression
int i = 1;
do {
// Loop body
cout << i << endl;
// Update expression
i++;
}while (i <= 5);
return 0;
}
Output
2
3
4
5
Nested Do-While Loop
You can nest one do-while loop inside another by simply writing the second do-while loop code inside the first do-while loop block. For example, the following code will explain how a nested loop works.
//A C++ program to show how a nested do-while loop works
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int j,i=1;
do {
do {
j=i;
cout<<j;
j++;
} while ( j<=5 );
cout<<endl;
i++;
} while ( i<=5 );return 0;
}
Output
2 3 4 5
3 4 5
4 5
5
Infinite Do-While Loop
An infinite Do-While loop can be due to a logical error or can be deliberately placed for a particular reason like waiting for the program to receive an input from a source and then continue execution. It can be achieved by either removing the exit condition or by not providing an update statement or even both.
//A C++ program to show how an infinite loop works
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i=1;
do { // No update statement
cout << "Hello World\n";
} while ( i<5 );
return 0;
}
Output
Hello World
Hello World
Ctrl + C
Example:2
//A C++ program to show how an infinite loop works
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i=1;
do { // Condition is always true
cout << "Hello World\n";
} while ( i>0 );
return 0;
}
Output
Hello World
Ctrl + C